XMR Adoption Persists Through Exchange Removals as Dark Web Platforms Embrace Monero
According to TRM Labs, Monero transaction volumes continue to exceed 2021 figures while underground marketplaces increasingly adopt XMR, and anomalous node patterns could provide law enforcement with network analysis opportunities.

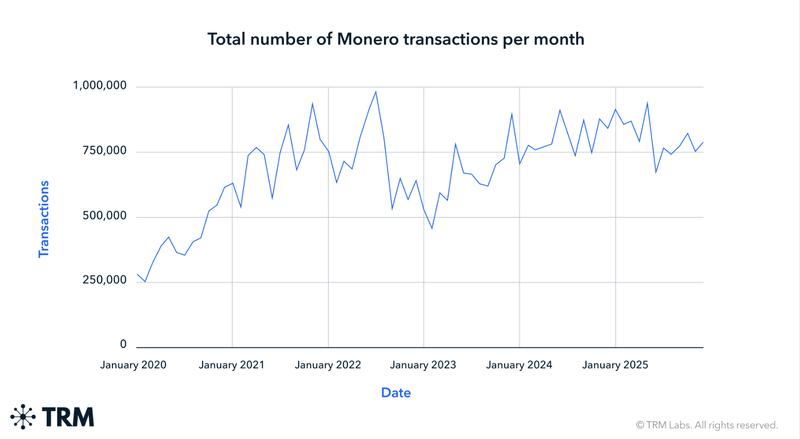
Despite widespread removals from leading cryptocurrency trading platforms, Monero continues to maintain consistent activity levels, according to fresh analysis published by TRM Labs.
The data indicates that transaction volumes throughout 2024 and 2025 have continued to exceed the levels recorded prior to 2022, implying that user demand has persisted even following the removal or limitation of the token by numerous prominent exchanges due to tracking and traceability issues, according to TRM Labs' research into market dynamics and the cryptocurrency's core network infrastructure.
Throughout 2024, leading cryptocurrency exchanges such as Binance and Kraken initiated efforts to remove or gradually eliminate Monero (XMR) from their platforms due to regulatory compliance challenges. The regulatory pressure intensified further this year when the financial oversight body in Dubai prohibited privacy-focused cryptocurrencies including Monero and Zcash (ZEC) from being traded on authorized platforms operating within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC).
The research findings additionally disclosed that Bitcoin (BTC) continues to serve as the dominant cryptocurrency for actual ransom payment transactions. While ransomware threat actors frequently demand Monero as payment and may even provide payment discounts for those choosing it, victims predominantly continue making payments using Bitcoin.
Nevertheless, underground marketplace platforms operating on the darknet seem to be trending in a different direction. The researchers discovered that 48% of darknet markets that launched in 2025 exclusively accepted Monero as payment, representing a "notable increase compared to earlier years," according to the research report.
Monero's privacy holds, but network may reveal clues
Although Monero's encryption technology successfully conceals transaction senders, receivers and transfer amounts, the research team looked past the blockchain itself to analyze how the network transmits transactions across the internet infrastructure. Their investigation revealed that approximately 14% to 15% of Monero network nodes demonstrated behavior patterns that differed from normal expectations, displaying atypical timing characteristics and connection clustering concentrated on specific server infrastructure.
This unusual behavior doesn't indicate that the network has been compromised through hacking. Rather, it indicates that certain operators might be running numerous interconnected nodes capable of monitoring how transactions propagate throughout the network system. Within peer-to-peer network architectures, computers that observe a transaction during its earliest propagation stages may obtain information about its original source location.
Although Monero's on-chain cryptography remains unchanged, network behavior can impact theoretical anonymity properties if observers can see message propagation.
Monero update targets "spy nodes"
During October 2025, the Monero development team released an updated software version designated as Fluorine Fermi (v0.18.4.3) designed to enhance user privacy protections and strengthen network security measures. This update implemented an improved peer-selection mechanism that directs user wallets away from questionable network segments and toward more trustworthy node connections.
The software upgrade specifically concentrates on defending against what the Monero community refers to as "spy nodes," terminology applied to individual nodes or coordinated groups of nodes attempting to correlate transaction data with users' IP address information. While these nodes cannot compromise Monero's cryptographic protections, they may potentially observe transaction propagation patterns throughout the network infrastructure.
Privacy-related concerns regarding the network infrastructure have been subjects of discussion within the community for multiple years. The matter received increased public attention following the leak of a 2024 video that implied investigators possessed capabilities to monitor network activity through deployment of their own observation nodes, which triggered substantial debate throughout the cryptocurrency community.