Bitcoin Mining Difficulty Plunges 11%+ in Largest Decline Since 2021 Chinese Crackdown
During China's 2021 cryptocurrency mining prohibition, the Bitcoin network experienced a mining difficulty reduction of up to 27% in a single adjustment cycle.

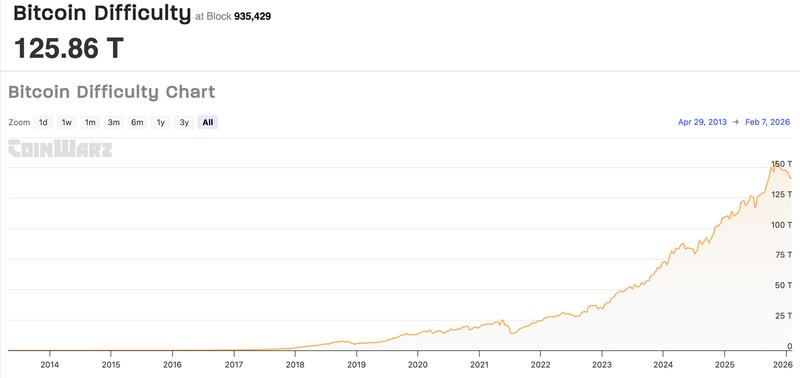
The mining difficulty of the Bitcoin network, which measures the complexity of appending new blocks to the Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain, declined by approximately 11.16% over the past 24 hours, marking the most significant reduction in a single adjustment cycle since China's 2021 prohibition on cryptocurrency mining activities.
The current Bitcoin mining difficulty stands at 125.86 T and became effective at block 935,429, according to information from CoinWarz. Block times are averaging more than 11 minutes, exceeding the protocol's 10-minute benchmark.
Projections indicate another decline in difficulty during the upcoming adjustment scheduled for February 23, with expectations of approximately a 10.4% decrease to 112.7 T, based on CoinWarz data.
The Chinese government declared a prohibition on cryptocurrency mining operations and commenced enforcement actions against digital assets in May 2021, which led to multiple downward difficulty adjustments occurring between May and July 2021, with reductions spanning from 12.6% to 27.9%, based on historical information from CoinWarz.
This significant downward adjustment occurred during a widespread cryptocurrency market decline, which saw Bitcoin's price plummet by more than 50% from its peak of over $125,000 to a bottom of $60,000, combined with a winter weather system affecting the US that resulted in temporary mining operation suspensions.
Winter Storm Fern sweeps through the US and curtails miner hashrate
An intense winter weather system moved across the United States during January, affecting 34 states spanning 2,000 square miles with accumulations of snow, ice and subfreezing temperatures that caused widespread electrical infrastructure disruptions.
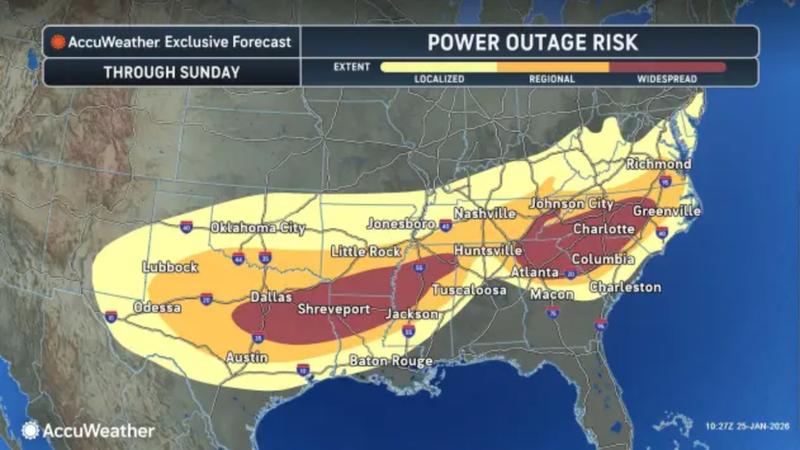
The interruptions to electrical grid systems forced Bitcoin mining operations based in the United States to temporarily reduce their power consumption and suspend activities, decreasing the overall network hashrate, which represents the computational capacity utilized by miners to maintain the security of the Bitcoin protocol.
Foundry USA, a mining pool based in the United States and currently the largest mining pool globally by hashrate, temporarily experienced a loss of approximately 60% of its hashing capacity during winter storm Fern.
The total hashing capacity of this mining pool dropped from approximately 400 exahashes per second (EH/s) to roughly 198 EH/s as a consequence of the weather event.
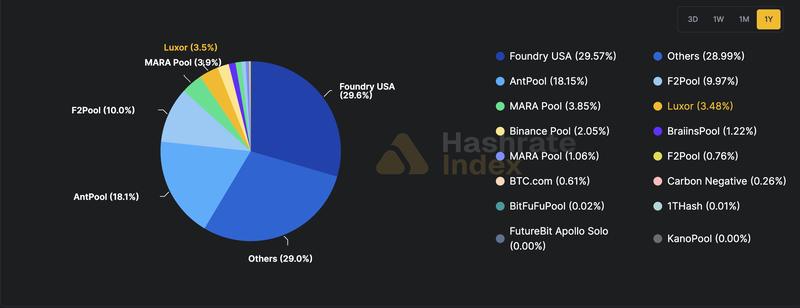
Foundry USA's hashrate has rebounded to above 354 EH/s, which represents the mining pool's current hashing capacity as of this report, and the pool continues to control 29.47% of the market share, based on data from Hashrate Index.
Nevertheless, the overall Bitcoin network hashrate fell to a four-month minimum during January due to worsening cryptocurrency market circumstances and mining operations transitioning to AI data center facilities and alternative high-performance computing applications.